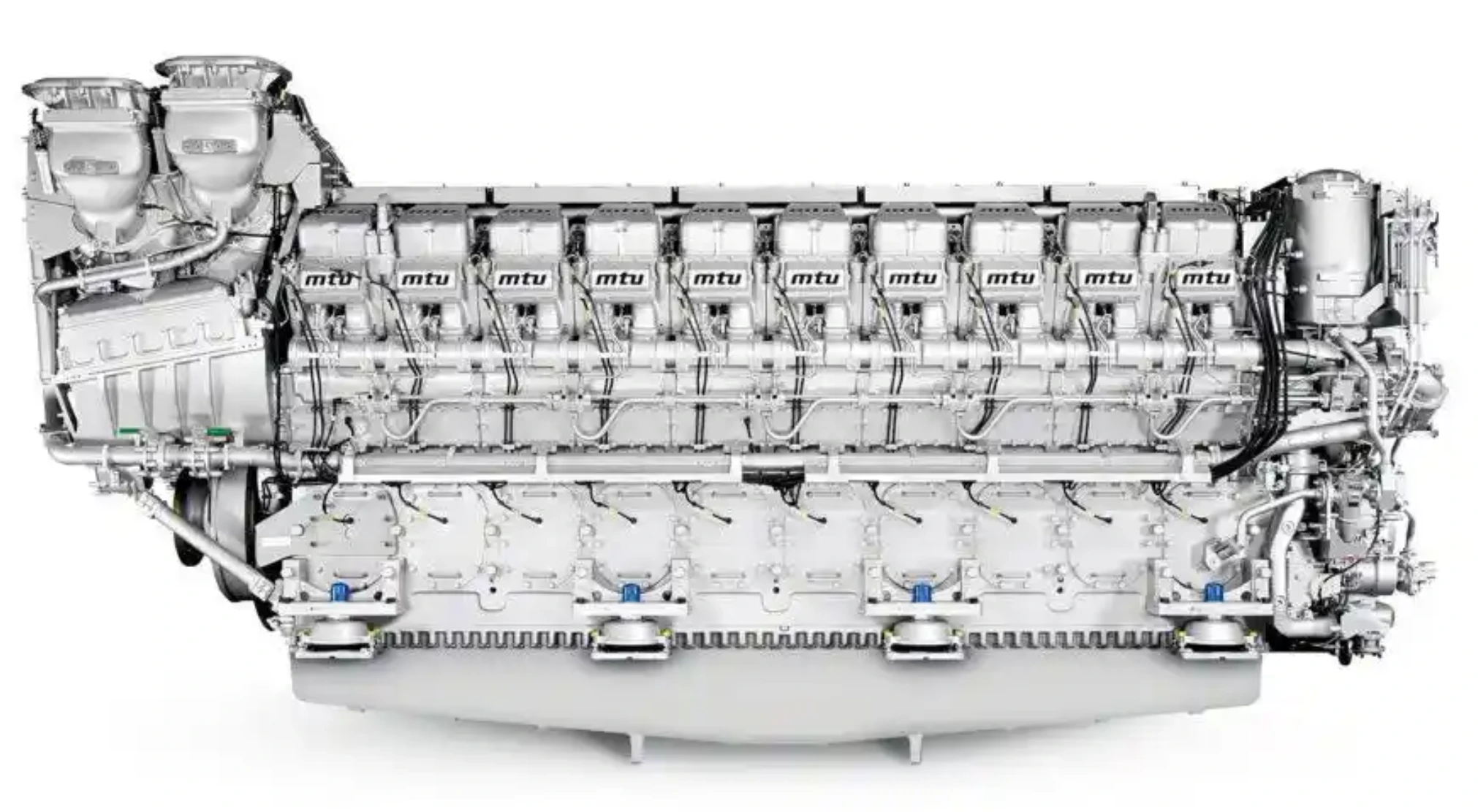
MARINE POWER UNIT SOLUTION MARINE DIESEL ENGINE)
Here are some of the world’s top marine diesel engine brands for your reference:
- Cummins
- Perkins
- Caterpillar
- MTU
- Volvo Penta
- Deutz
- MAN
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Doosan
- WinGD
- Weichai
- Yuchai
Features
Marine Power Unit (Marine Diesel Engine and Gearbox Unit)
The marine diesel engine gearbox unit is a core component of a ship's propulsion system, primarily used to efficiently transmit the power from the diesel engine to the propeller, ensuring the vessel's propulsion and maneuverability.
Composition and Structure
The marine diesel engine gearbox unit typically consists of the following components:
- Diesel Engine: The core power-generating equipment that converts fuel combustion into mechanical energy.
- Gearbox: Adjusts the output speed and torque of the diesel engine through gear transmission to match the propeller's requirements.
- Coupling: Connects the diesel engine and gearbox, transmitting power and absorbing vibrations.
- Control System: Monitors and regulates the unit's operating conditions to ensure safety and efficiency.
- Cooling System: Dissipates heat to prevent equipment overheating.
Working Principle
- The diesel engine generates power, which is transmitted to the gearbox via the coupling.
- The gearbox adjusts the speed and torque as needed and delivers the output to the propeller.
Key Features
- Efficient Power Transmission: The gearbox optimizes power output, improving fuel efficiency.
- High Reliability: Designed to withstand harsh marine environments, ensuring long-term stable operation.
- Operational Flexibility: Supports forward, reverse, and neutral operations, facilitating vessel control.
- Compact Structure: Saves space, making it suitable for the limited environment on ships.
Applications
- Commercial Ships: Such as cargo ships, oil tankers, and passenger ships.
- Fishing Vessels: Used for fishing operations.
- Engineering Ships: Such as dredgers and crane vessels.
Technical Parameters
- Power Range: From tens of kilowatts to tens of thousands of kilowatts.
- Speed Range: From hundreds to thousands of revolutions per minute (RPM).
- Gear Ratio: Designed based on requirements, typically ranging from 1:1 to 10:1.
Maintenance and Care
- Regular Inspections: Including checks on lubricating oil, gear wear, and couplings.
- Lubrication Management: Regularly replace lubricating oil to ensure the lubrication system functions properly.
- Vibration Monitoring: Periodically detect vibrations to prevent abnormal wear.