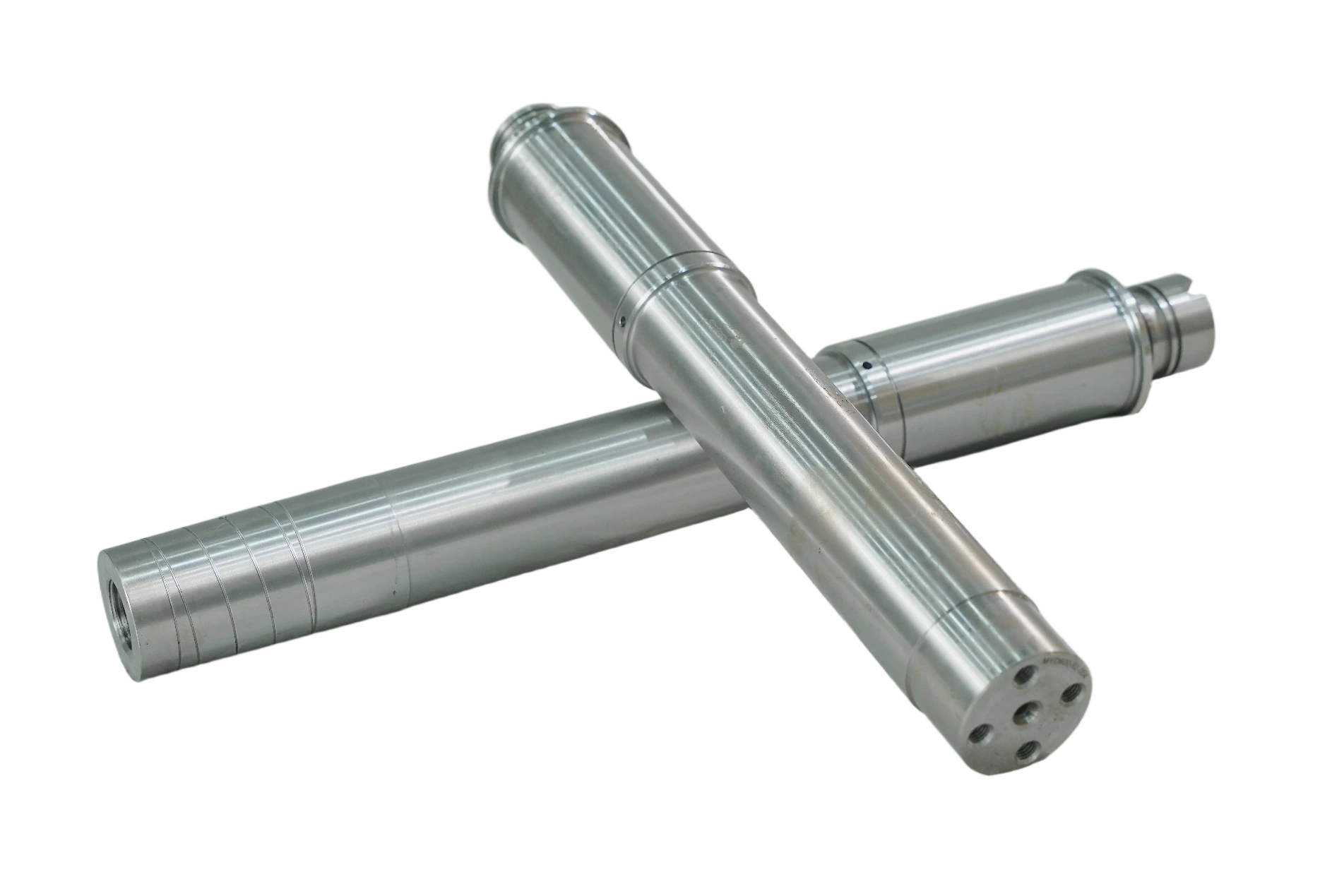
INTERMEDIATE SHAFT OF MARINE GEARBOX INTERMEDIATE SHAFT
Features
Material
The input shaft is typically made of high-strength alloy steels, such as:
- 20CrMnTi: A carburizing steel with high strength and wear resistance.
- 42CrMo: A quenched and tempered steel with excellent comprehensive mechanical properties.
- 40Cr: A quenched and tempered steel with balanced strength and toughness.
Heat treatment
- Carburizing and Quenching: Suitable for 20CrMnTi, where the surface is carburized and then quenched to achieve high surface hardness while maintaining a tough core.
- Quenching and Tempering: Suitable for 42CrMo and 40Cr, where the material is quenched and then tempered at high temperatures to achieve good overall mechanical properties.
- Surface Hardening: Achieved through induction hardening or flame hardening to improve surface hardness and wear resistance.
Processing
- Rough Machining: Forging the blank followed by rough turning, leaving machining allowances.
- Semi-Finishing: Semi-finish turning of the outer diameter and end faces to ensure dimensional and geometric tolerances.
- Heat Treatment: Carburizing and quenching or quenching and tempering, depending on the material.
- Finishing: Precision turning of the outer diameter and end faces, and grinding of critical areas to ensure dimensional accuracy and surface roughness.
- Surface Treatment: Such as chrome plating or nitriding to further improve wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
- Inspection: Including dimensional checks, hardness testing, and non-destructive testing to ensure quality compliance.